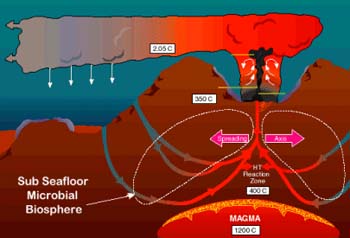
The upflow
zone is the path to the exit, where heated, buoyant hydrothermal fluids
ascend rapidly to the seafloor vents. The reaction zone is located just
above the molten (or partially molten) rock in the volcanic system. In
cases like Axial Seamount and also many mid-ocean ridge segments, magma
resides at 1-4 km depth within the oceanic crust, and the long-term location
of the reaction zone is just above the magma, at the base of the dikes
which form most of the upper crust. Fluids reach temperatures of up to
450°C,
and pick up a heavy load of dissolved metals from reaction with the surrounding
rock.
In the
upflow zone, hot, buoyant hydrothermal fluids race to the seafloor. In
some cases the fluid path is not well focused, especially after a disruption
to the system such as an eruption. The fluids may mix with seawater before
they reach the seafloor, cooling down and spreading out to produce diffuse
venting. In other cases, the fluids take a direct path to the vent with
little or no mixing and exit the seafloor at temperatures as high as 300-400°C.
The magma
reservoir acts as a stable long-lived heat source for hydrothermal circulation,
and indeed the presence of long-lived hydrothermal activity seems to reflect
the presence of a substantial magma body at depth. Individual lava flows
and dikes are small in volume by comparison, and are cooled within a few
months to a few years after an eruption. Nevertheless, they support or
augment wide-spread but short-lived diffuse venting. On the 1998 lava
flow at Axial, a majority of the diffuse vents located in 1998 had already
shut down by the summer of 2000. Those that remain vigorous, including
the Marker 33/Cloud Vent area, are located near the 1998 eruptive fissure.
In contrast, the 1998 eruption served to rejuvenate the preexisting, long-lived
high temperature vents at ASHES and CASM. These focused vent sites are
both located near the caldera fault system of Axial, with CASM actually
at the intersection of caldera wall and the north rift zone.
|